DK Goel Accountancy Class 11 Solutions Chapter 25 Introduction to Accounting Information System from the new edition of DK Goel Class 11 Accountancy textbooks is outlined by expert Accountancy teachers. MNS EdTech offers DK Goel Solutions to help students understand all of the theories in particular. There are several definitions in accounting, but the Trial Balance, Depreciation, and Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) are all necessary.
DK Goel Accountancy Class 11 Solutions – Chapter 25
Question 1
How are computer and accounting?
Answer: The computer, an electronic device which computes, modifies, compares, retrieves and stores the facts, is being widely used in the field of accounting. It has an inbuilt system of making arithmetical calculations, collecting and processing accounting data and presenting the outcomes in the form of reports to the management for decision-making purposes.
Question 2
Depict the organisational levels in the form of a diagram.
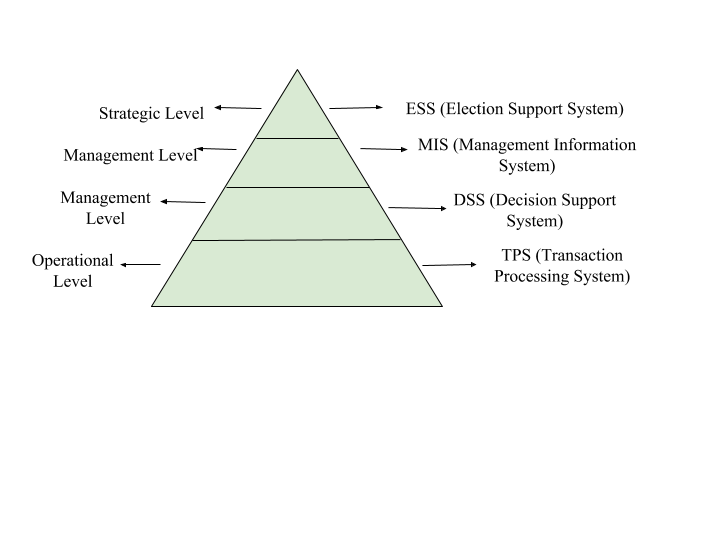
Question 3
Explain any six purposes of accounting information system.
Answer
The six purposes of an accounting information system are.
- Sales Order Processing- It is one of the important transaction processing systems which prepares buyers order and produces invoices for them and data needed for sales analysis and inventory control.
- Inventory Control- It is used to keep a record of various levels of inventory and changes happened to it.
- Accounts Receivable- This system is used to track the amount owed by the buyers.
- Accounts Payable- This is used to record data related to all the purchases from the supplier and payment done by them.
- Payroll- This system records data from employees time card. It is used in producing employees documents like salary statement, payroll reports, labour analysis report, etc.
- General Ledger- The general ledger system consolidates the data received from accounts receivable, account payable, payroll, and other accounting information systems.



0 Comments